- The Intelligence
- Posts
- ☢️ AI to build nuclear power plants ☢️ Week 51
☢️ AI to build nuclear power plants ☢️ Week 51

☢️ AI to build nuclear power plants ☢️
Good afternoon.
Yeah, you saw that right. Microsoft is planning on getting AI involved with building nuclear power plants. What could go wrong…? 🙄
Let’s dive right into this week’s newsletter packed with updates and tips.
Table of contents
Using your prompt as a lever 🕹️
🔋 Nuclear power plants build by AI ☢️
TikTok parent company secretly using OpenAI tech 👀
OpenAI turning into a news channel? 📺
💻 A $2B AI startup from France 💸
New Google AI tools
✨ How to improve your ChatGPT output [Part 3]✨
Even after giving the perfect prompt and using the right extra techniques to make sure the output is good, it still sometimes happens that ChatGPT is just a little too much.
Don’t worry, we also got something to tackle this. After this three part series about prompting you’ll be the best prompter in town 😎
All you have to do is to make a scale where you define 1 and 10.
“On a scale of 1-10.
If 1 is X
And 10 is Y
How much would you rate your answer?”
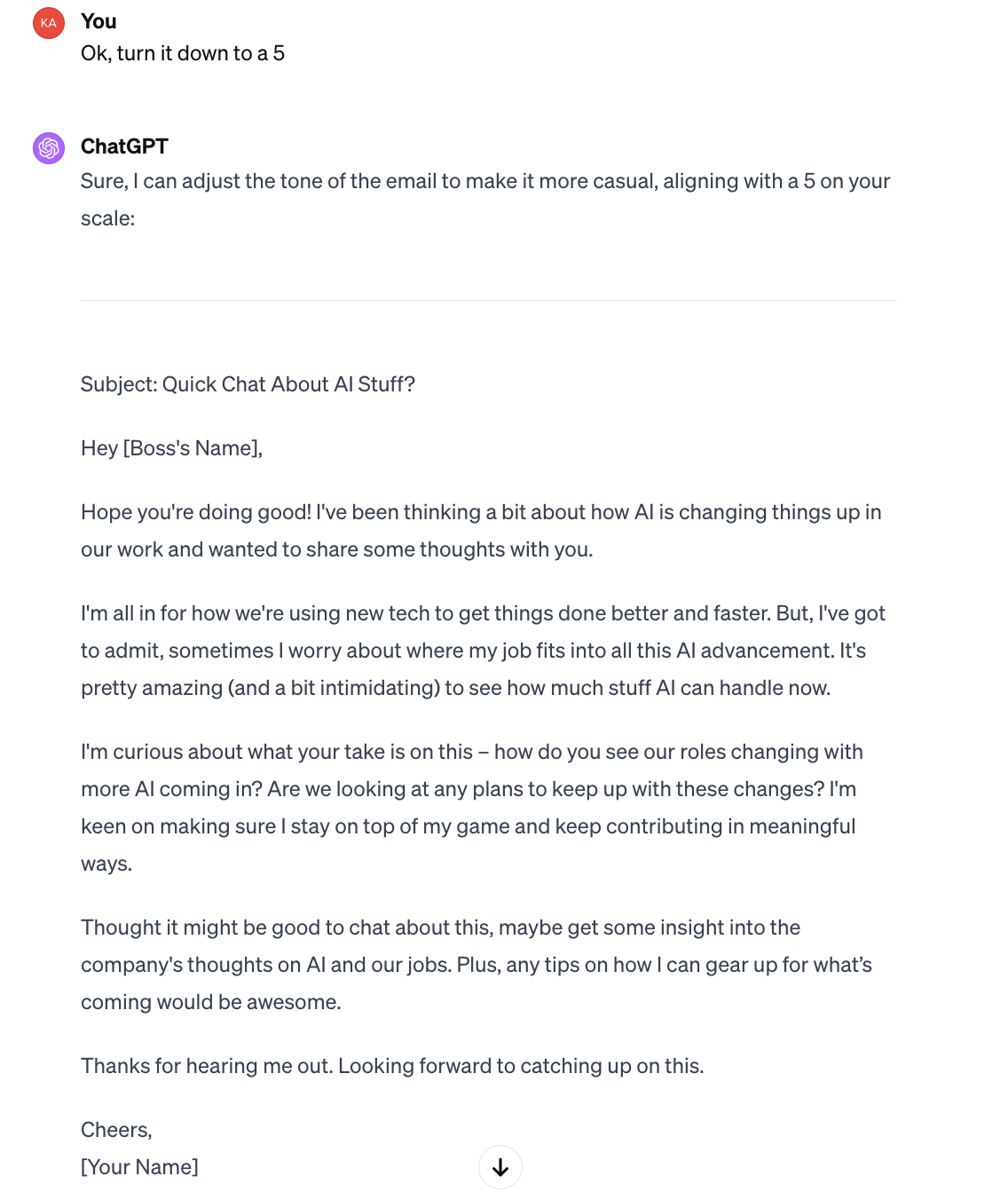
Look at the difference in output:
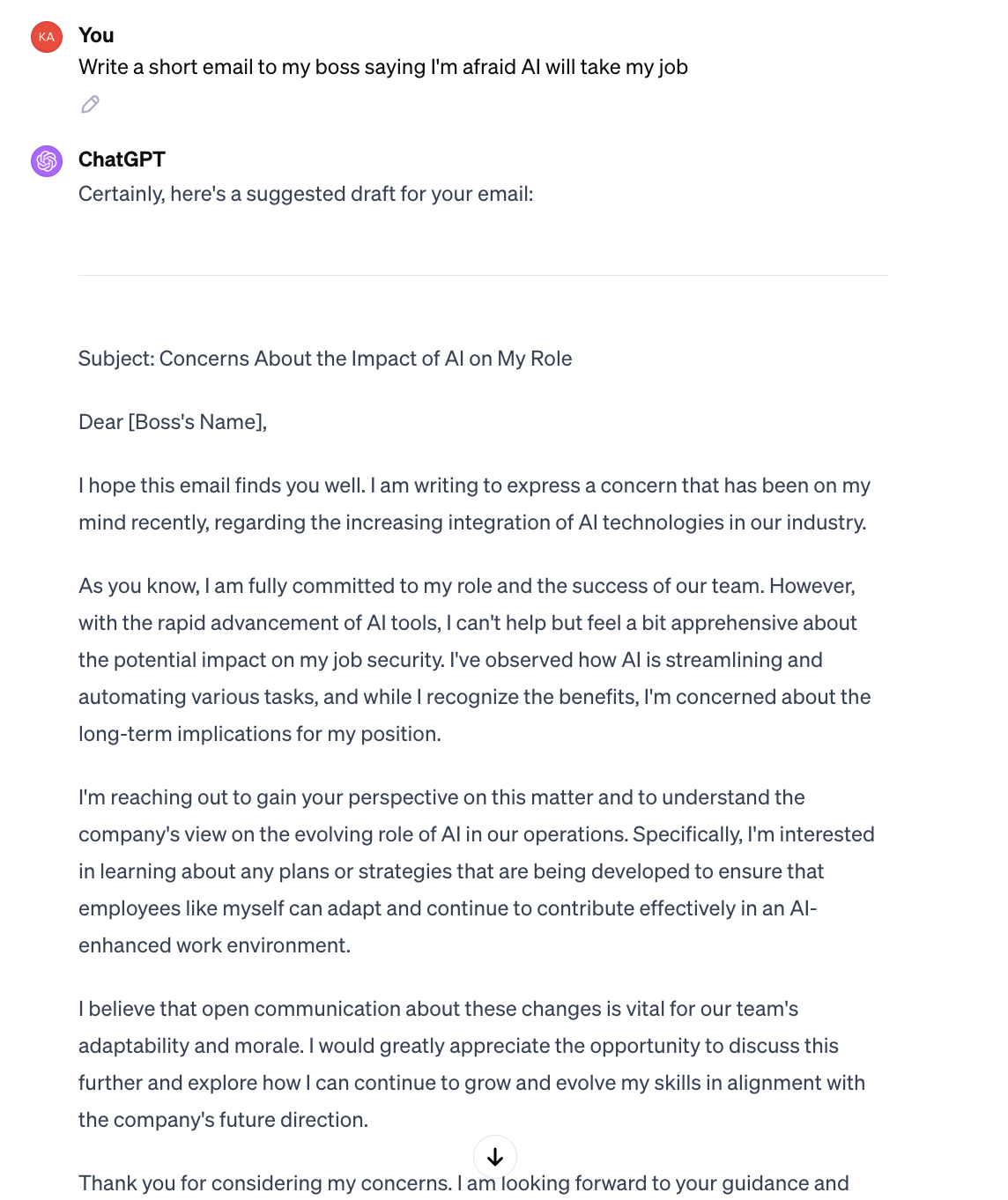
You use the lever prompt
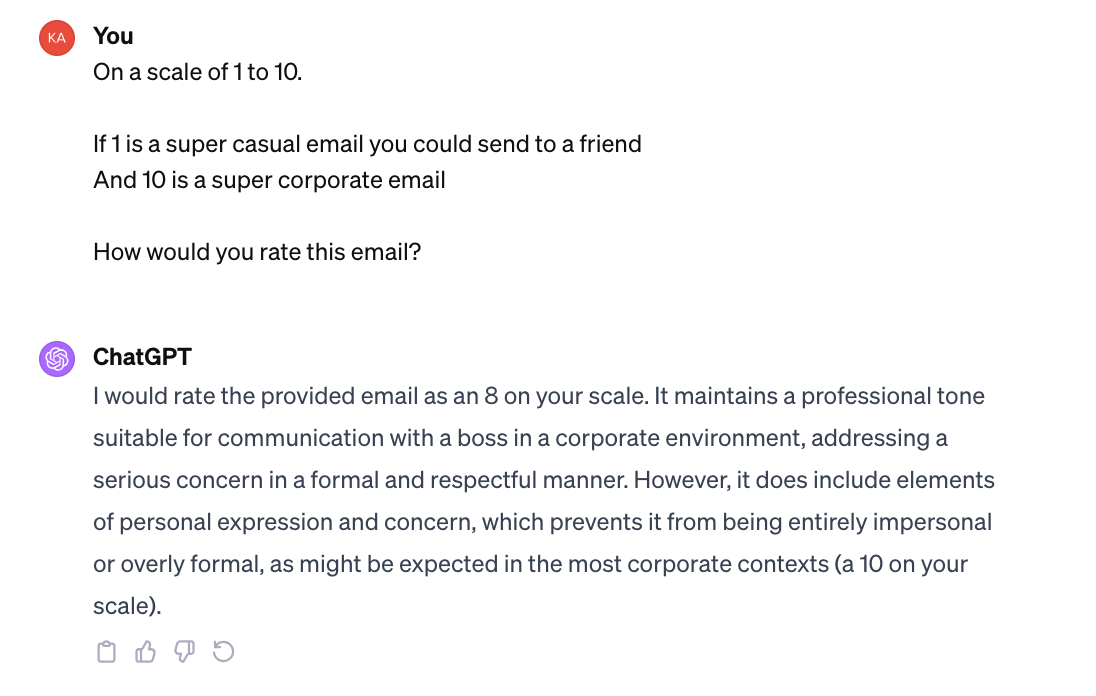
Look at the difference
Updates
Nuclear power plants build by AI
Tech giant Microsoft is training an AI to handle the paperwork for setting up new nuclear power plants, aiming to expedite the approval process and reduce costs associated with traditional methods. The company is working with a large language model, which has been trained on US nuclear regulatory and licensing documents for the past six months. The goal is to cut down the human hours required for approval, which can take years and cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
Instead of relying solely on solar and wind power, tech companies like Google and Microsoft are increasingly turning to small modular reactors (SMRs), which are scaled-down power plants that aim to reduce construction costs through standardization of components and systems. However, there are currently no SMRs in operation in the US, and permitting and construction for SMRs remain expensive.
Despite the potential risks associated with AI handling nuclear regulation paperwork, the company is confident that it is doing its homework to ensure the AI does not trigger a nuclear meltdown. Terra Praxis, a nonprofit partnering with McDonald's, assures that the AI is not hallucinating and is being trained on specific, highly structured documents to produce similar documents.
TikTok parent company secretly using OpenAI tech
ByteDance, known for its popular app TikTok, has been reportedly engaging in clandestine activities to develop a rival to ChatGPT, a product of OpenAI. This undertaking, referred to as 'Project Seed', has led to significant repercussions.
Here are the key points of the situation:
'Project Seed', a large language model (LLM) project by ByteDance, extensively utilized OpenAI's API during its developmental stages.
The initiative, which started approximately a year ago within ByteDance, has been a top-secret and high-priority project.
The primary team working on Project Seed is based in China, although it includes members from the United States as well.
ByteDance's actions have been deemed a breach of OpenAI's terms of service, resulting in the suspension of their developer account with OpenAI.
An inside source suggested that ByteDance's aim was to ensure legal compliance, but their main concern appeared to be avoiding detection, which ultimately did not succeed.
This incident highlights the extraordinary lengths a major corporation has gone to in its efforts to compete in the advanced AI sector.
OpenAI turning into a news channel?
OpenAI has reached an agreement with Axel Springer, the Berlin-based owner of publications including Business Insider and Politico, to train its generative AI models on the publisher's content and add recent Axel Springer-published articles to OpenAI's AI-powered chatbot ChatGPT. Key points of the deal include:
The agreement is OpenAI's second such arrangement with a news organization, following a deal with The Associated Press to license some of its archives for model training.
ChatGPT users will receive summaries of "selected" articles from Axel Springer's publications, including stories normally gated behind a paywall, accompanied by attribution and links to the full articles.
Axel Springer will receive payments of an unspecified size and frequency from OpenAI in return for the rights to use its content.
The deal is valid for several years and does not commit either side to exclusivity
Axel Springer plans to support OpenAI's existing AI-driven ventures "that build upon OpenAI's technology".
This partnership comes amid a broader debate over the use of copyrighted material in training generative AI models, with publishers alleging copyright infringement and expressing concerns about potential reductions in traffic to their websites.
🛠️ Tool of the week 🗓️
Scribe introduces a way to create step-by-step guides without the hassle of manually documenting each step. This innovative tool eliminates the need for tedious video calls to explain processes to colleagues. With Scribe, you can effortlessly produce a comprehensive guide simply by performing the task you wish to explain.
Key Features of Scribe:
Automated Process Documentation: Scribe's technology automatically captures the steps you take during a process, effectively documenting it without requiring your direct input.
Effortless Sharing: Once a step-by-step guide is created, Scribe provides a shareable link. This means you can easily distribute the guide to others, saving time and avoiding repetitive explanations
User-Friendly Guides: The output is a well-organized, easy-to-follow step-by-step guide, making it accessible and understandable for everyone, regardless of their familiarity with the process.
Scribe essentially streamlines the way we communicate and teach processes, making it an invaluable tool for workplaces and educational environments alike.
More updates
A $2B AI startup from France
Mistral AI, a Paris-based start-up founded seven months ago by researchers from Google and other tech giants, has raised €385 million ($415 million) in funding, valuing the company at about $2 billion. The company builds technology that businesses can use to deploy chatbots, search engines, online tutors, and other AI-driven products. Mistral is among a small group of companies that are developing AI technology that could rival that of OpenAI, the San Francisco start-up that gained fame with the release of the ChatGPT chatbot.
Mistral's approach to AI is based on the open-source model, which allows others to freely copy, modify, and reuse the technology. This approach is seen as a safer path because more people can review the technology, find its flaws, and work to remove or mitigate them. Rival companies like OpenAI and Google argue that the open-source approach is dangerous and that the raw technology could be used to spread disinformation and other harm material.
The start-up's valuation has increased more than sevenfold in just six months, and its technology has been released as open-source software. Mistral's success has taken on considerable importance in France, where leaders like Bruno Le Maire, the finance minister, have pointed to the company as providing the nation a chance to challenge U.S. tech giants. Europe has not produced many meaningful tech companies since the dot-com boom and sees artificial intelligence as a field where it can gain ground. Investors are also pumping money into other start-ups that believe in the open-source approach, such as Perplexity, which has raised a new $70 million funding round that values the company at $500 million.
New Google AI tools
Google has unveiled AlphaCode 2, an improved version of the code-generating AlphaCode introduced by Google’s DeepMind lab roughly a year ago. AlphaCode 2 is powered by Gemini, or at least some variant of it (Gemini Pro) fine-tuned on coding contest data. AlphaCode 2 can understand programming challenges involving “complex” math and theoretical computer science. It is capable of dynamic programming, which entails simplifying a complex problem by breaking it down into easier sub-problems over and over.
Google also introduced Imagen 2, the second generation of its AI model that can create and edit images given a text prompt. This new model, developed using technology from Google DeepMind, offers improved image quality and new capabilities, including the ability to render text and logos. It can render text in multiple languages and overlay logos in existing images. Imagen 2 can also understand more descriptive, long-form prompts and provide detailed answers to questions about elements in an image.